What does Mudra mean?
Mudras — meaning ‘seal’, mark’ or ‘gesture’ in Sanskrit — are said to intensify the effects of our yoga or meditation practice and enhance the flow of energy. A mudra is a sacred and symbolic gesture found in yoga, Buddhism, Hinduism and Jainism. The most well-known mudras are used during yoga and meditation practice as a means of channeling the flow of vital life force energy known as prana.
There are believed to be around 400 known mudras. Each individual mudra has unique symbolism and is thought to have a specific effect on the body and mind by clearing energetic pathways. Although hand (hasta) mudras are the most common in yoga, there are also body (kaya) and consciousness (citta) mudras.
Traditionally, these mudras were practiced only by accomplished masters known as siddhas, and were kept secret from regular practitioners.
The most commonly used hasta mudras are :
1. Jjana mudra (Gyan Mudra)

Also known as chin mudra, this is arguably the most well-known of all mudras, practiced in Buddhism, Hinduism and yoga. In gyan mudra, the tip of the thumb and index finger touch, the other three fingers extend and the palms face upward. It is believed to help still the mind and is therefore commonly used for meditation.
Benefits of Gyan Mudra :
- Better retention and concentration power.
- Improves sleep pattern.
- Increases energy in the body.
- Alleviates lower backache.
2. Dhyana mudra:
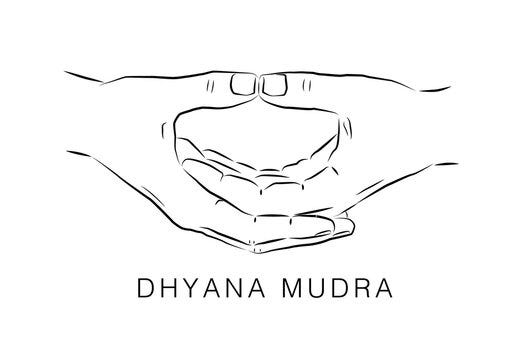
Otherwise known as meditation mudra, this gesture is famous for having been practiced by the Buddha at the time of his enlightenment. This mudra is performed with the right hand resting on top of the left, palms facing up and tips of the thumbs touching.
Benefits of Dhyana Mudra :
- The practice of Dhyana Mudra brings a sense of calm and harmony with the mind, hence can be done by students who are restless, irritated, irritable, or fidgeting in nature.
- With better control over the mind, it helps to keep anger in control, keeps negative thoughts away, increases confidence level, better memory, helps to control bad dreams, etc.
- On a spiritual level, the practice of Dhyana Mudra helps students to build self-awareness, seeking for answers, going inwards, intuition, insight, etc.
- Dhyana Mudra (Yoga Mudra) has a deep impact on controlling the stress levels in the body, hence is practiced to keep anxiety and depression in control.
3.Anjali mudra:

This mudra is often used as a salutation at the beginning and end of a yoga class. Also known as prayer position, the palms are brought together in front of the sternum with the fingertips pointing upwards.
Benefits of Anjali Mudra :
- Provides flexibility in the wrists and arm joints.
- Stimulates the anahata chakra.
- In the extended practice it stimulates and activates ajna chakra.
- Calms mind.
- Relieves stress.
- Improves focus.
- Promotes inner awareness.
- Connects the hemispheres of the brain and optimizes brain functions and coordination.


